|
|
|
|
|
Magnetic
Resonance Force Microscopy |
|
Results |
|
|
Navigation ● Results ● Seminars ● Talks ● News ● Contacts |
Results |
|
|
|
|
MFM study of magnetic skyrmion lattice Co/Pt multilayers
with perpendicular magnetic anisotropy are irradiated by focused He ion beam to locally reduce the anisotropy value. The
irradiated spots with a diameter of 100 nm are arranged in a square lattice
with 200 nm period. The formation of the nonuniform
periodic magnetic structure is observed without changes in the film
topography. The spatial symmetry of the magnetic force microscopy signal and
the specific shape of magnetization curves indicate the formation of the magnetic
bubbles or magnetic vortices within the irradiated spot depending on the
irradiation dose. The experimental data are in a good agreement with micromagnetic simulations of the system.
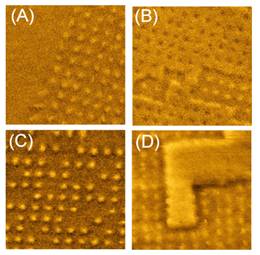
Fig. The MFM image of the samples at large (A and B) and small (C and
D) radiation doses, respectively, in residual (A and C) and demagnetized (B
and D) states. The scan area is 2 × 2 μm2. M. V. Sapozhnikov, S. N. Vdovichev, O. L. Ermolaeva, N. S. Gusev, A. A. Fraerman, S. A. Gusev, and Yu. V. Petrov -Artificial dense lattice ofmagnetic bubbles, Applied Physics Letters, 109, 042406 (2016) <pdf> Ferromagnetic resonance in CoPt/Co system We report a study of interlayer
exchange interaction in multilayer [Co/Pt]n/Pt/Co
structures. The structures consist of a periodic [Co/Pt]n
multilayer film with a perpendicular anisotropy and a thick Co layer with an
in-plane anisotropy. The subsystems are separated by a Pt spacer with
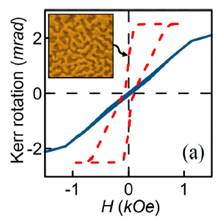
variable thickness. The magnetooptical Kerr effect
and the ferromagnetic resonance measurements show the essentially
non-collinear state of magnetic moments of the layers and strong exchange
coupling between the [Co/Pt]n and the Co
subsystems. A simple model based on the Landau-Lifshitz-Gilbert
equation shows that the exchange coupling is ferromagnetic. The exchange
constant is estimated in this simple model. The estimated value is J = 2 erg/cm2.
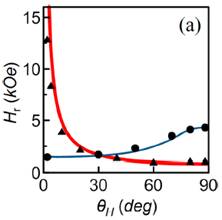
Fig. Hysteresis
loops and angle dependences of the resonant fields of the CoPt/Co system. E. S. Demidov, N. S. Gusev, L. I. Budarin, E. A. Karashtin, V. L. Mironov and A. A. Fraerman - Interlayer interaction in multilayer [Co/Pt]n/Pt/Co structures, Journal of Applied Physics, 120, 173901 1-4 (2016). <pdf> Ferromagnetic resonance in locally modified CoPt
films We study the dynamical properties of a magnetic film
with spatially modulated perpendicular anisotropy by numerical simulations.
Both topologically charged states (magnetic skyrmions)
and uncharged uniform and nonuniform states are
considered. The dependences of the ferromagnetic resonance (FMR) spectra on
the geometry and material parameters of the system are analyzed. It is found
that the spectra contain resonances of the localized and delocalized modes of
the magnetization oscillations. In the case of nonuniform
states the localized modes have the form of rotating magnetization
distributions. The direction of the rotation depends on the local density of
the toroidal moment of the state. The magnetic
states with different FMR spectra can be easily switched by a temporary
applying of a uniform external magnetic field that can be used in the tunable
microwave devices.
Fig. Oscillation modes of CoPt
modified regions. M. V. Sapozhnikov, R. V. Gorev, E. A. Karashtin and V. L. Mironov – Spin-wave resonances of ferromagnetic films with
spatially modulated anisotropy,
Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 466, 1-6 (2018). <pdf> Ferromagnetic resonance in interacting magnetic microstripes The results of the micromagnetic
simulation of forced oscillations of the magnetization in a system of two
interacting microstrips located at an angle to each
other have been presented. The ferromagnetic resonance spectra and the mode
composition of resonant oscillations of the system have been investigated
under the conditions of magnetostatic and exchange
interactions between the microstrips. It has been
shown that the magnetostatic interaction leads to
the possibility of the excitation of in-phase and out-of-phase coupled
oscillations of the magnetization of the microstrips.
In the systems of exchange-coupled microstrips,
there are intense resonances due to oscillations of the domain walls. The
transformation of the ferromagnetic resonance spectrum and the change in the
mode composition of resonant oscillations in different equilibrium configurations
of the magnetization of the system have been discussed, as well as the
conditions for the excitation of oscillations of different types depending on
the direction of the microwave magnetic field.
Fig. Resonance oscillations of NiFe
system of NiFe interacting microstripes
with domain wall. R.V. Gorev, E.V. Skorokhodov
and V.L. Mironov – Ferromagnetic resonance in interacting
magnetic microstripes, Physics
of the Solid State, Vol. 58, No. 11, pp. 2212-2217 (2016). <pdf> Ferromagnetic resonance of a magnetostatically stabilized domain wall in a nanowire-nanoparticle planar system The results of micromagnetic
simulation of induced high-frequency magnetization oscillations in a planar
ferromagnetic system composed of a magnetostatically
coupled nanowire and nanoparticle
are reported. The possibility of transformation of the spectrum of this
system by introducing a domain wall stabilized with the magnetic field of the
nanoparticle into the nanowire
is discussed. The dependences of the frequency and amplitude of resonant
oscillations of the domain wall on the geometric parameters of the system are
analyzed.
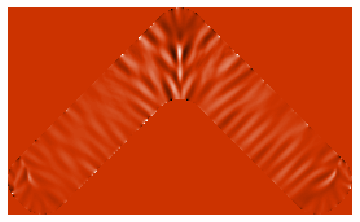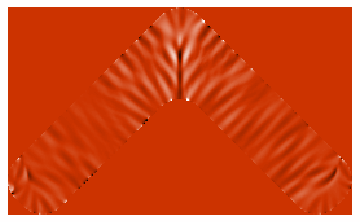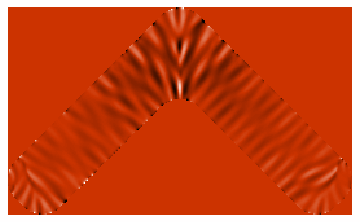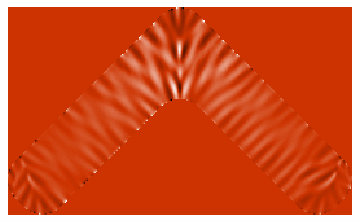
Fig. FMR of transverse and vortex domain walls in nanowire. R.V. Gorev,
V.L. Mironov – Ferromagnetic resonance of a magnetostatically stabilized domain wall in a nanowire-nanoparticle planar system, Technical Physics Letters, Vol. 43, No. 3,
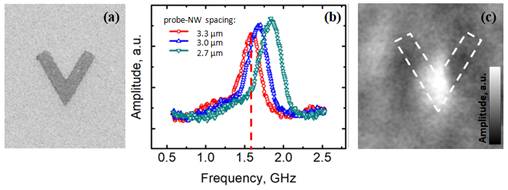
pp. 254-257 (2017). <pdf> Ferromagnetic resonance force microscopy of individual domain wall We report on ferromagnetic resonance force
microscopy (FMRFM) based investigations of the ferromagnetic resonance of a
single domain wall (DW) in a V-shaped planar permalloy
nanowire (NW) which is bent by 60[1].
A pronounced resonance associated with the DW is observed at 1.6 GHz. FMRFM
imaging at the resonance frequency confirms the localization of the resonant
mode in the DW area. The measured spectra and spatial distribution of the
resonant signal are in good agreement with the results of micromagnetic
modeling. Published by AIP Publishing.
A. Volodin, C. Van Haesendock, E. V. Skprpkhodov,
R. V. Gorev, V. L. Mironov – Ferromagnetic resonance force microscopy of individual
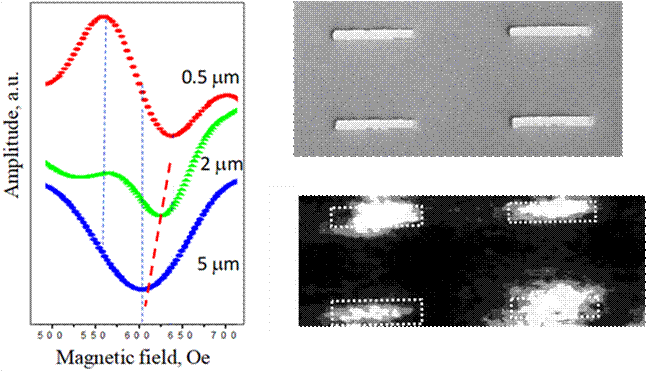
domain wall, Applied Physics Letters, 113, 122407, 1-4 (2018). <pdf> MRFM of dense array The ferromagnetic resonance in an array of permalloy
microstrips 3000 × 500 × 30 nm in size ordered on a
rectangular grid 3.5 × 6 μm in size has been investigated by magnetic resonance force microscopy.
The dependences of magnetic resonance force microscopy spectra of a sample on
the probe–sample distance are analyzed. The possibility of detection of a
ferromagnetic resonance spectrum of a single microstrip is demonstrated.
E.V. Skorokhodov, M.V. Sapozhnikov and V.L. Mironov – Magnetic Resonance Force Microscopy of a Permalloy
Microstrip Array, Technical Physics
Letters, Vol. 44, No. 3, pp. 203-206 (2018).
<pdf> |
|
|
Web site was developed by Victor L. Mironov |
|